Lowering the LCP Value in a Shopify App
TL;DR — Two attempts are made at reducing the LCP for a Shopify app. Serving the app from a CDN did not work. Splitting the code into smaller bits did.
LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) is a critical performance metric originally employed by Google to evaluate a web page’s loading performance. In essence, LCP calculates the time elapsed from when a page starts loading until the largest content element on the screen becomes visible, which could be in the form of images or text blocks.
An LCP value of 2.5 seconds or less signifies a good user experience. However, achieving and maintaining an optimal LCP value is imperative for Shopify apps, as this allows them to qualify for Shopify’s “Built for Shopify” badge, signifying excellent performance standards.
About RealtimeStack
RealtimeStack is a Shopify application that offers merchants real-time updates of customer activity in their store. Through various data visualizations, such as 3D live views, map views, and tables, the app enables store owners to gain insights into customer behavior and interactions. Developed using TypeScript, React, and Vite, RealtimeStack is hosted on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) and leverages pubsub, firestore, and a self-hosted PostgreSQL database for backend operations.
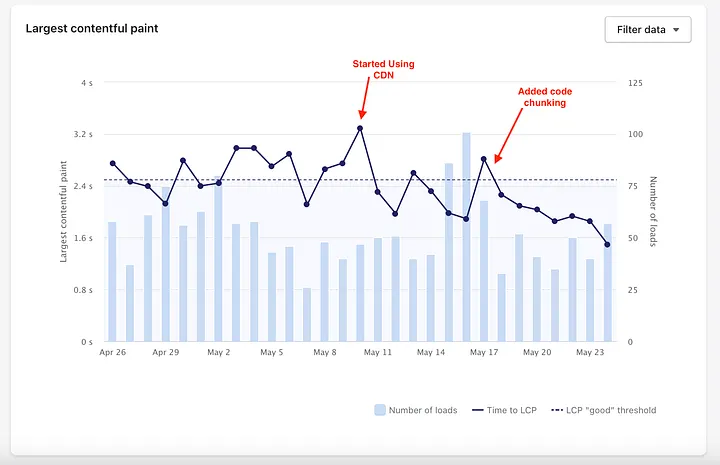
The LCP value of RealtimeStack was initially found to exceed 2.5 seconds, with substantial fluctuations hampering its performance, as seen here:
One general issue with the app is that it uses “heavy” libraries on the frontend — in particular Three.js for 3D views, and Mapbox for map views. These libraries increase the overall size of the React app, leaving it around 4.5MB.
Approach 1: Serving the React App from a CDN
The first step undertaken to decrease the LCP value involved serving the RealtimeStack app’s React application from a Content Delivery Network (CDN) rather than a US-based server. Utilizing Google’s Cloud CDN service proved advantageous, as it allowed the app assets to be cached globally and served faster to end-users by reducing latency.
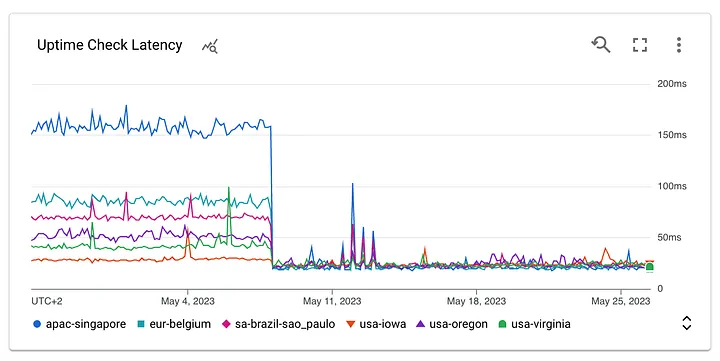
Implementing this change was relatively straightforward, as it merely involved configuring the GCP bucket to enable Google’s Cloud CDN service. Although this approach led to an improvement in the LCP value, it remained higher than the desired threshold, with fluctuations still posing a critical concern.
This was a bit surprising to me, since the latency improvement looked promising in the graph. OK — so it was not the speed — let’s go for the size!
Approach 2: Code Splitting and Reducing Initial Chunk Size
The second strategy required a more meticulous examination of the application code. The app has been designed in a modular approach, with a custom-built display library that takes up the majority of the code. When the app starts, one of the first things it does is establish a websocket connection to the backend. This connection code was also part of the display library (yes, not exactly clever design from my side), meaning that the display library would be loaded even though the majority of it was not used.
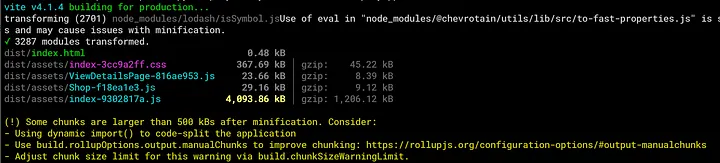
Ouch, 4MB — Vite cannot split the index.js code any further, since the display library is needed on initial load
To address this issue, I dissected the display library to ensure that the initial page would not load the 3D libraries and Mapbox components, as they weren’t required immediately upon loading. As a result, the initial page size dropped dramatically from over 4 MB to less than 1 MB.
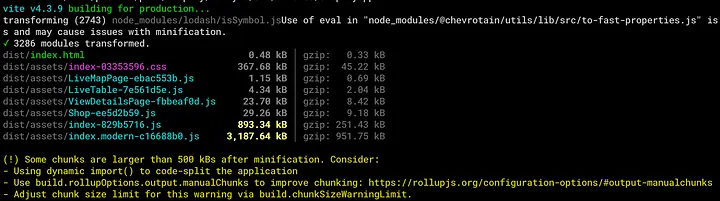
Ahh, much better. The index.js file is now less than 1MB — and the larger index.modern file is only loaded on demand
Lazy loading of pages was done via React’s lazy() API.
This optimization had a notable impact on the application’s LCP value, which successfully reduced to approximately 1.7 seconds. Moreover, fluctuations in the LCP value were considerably mitigated, thereby enhancing the overall performance and user experience of the RealtimeStack app.
Success!
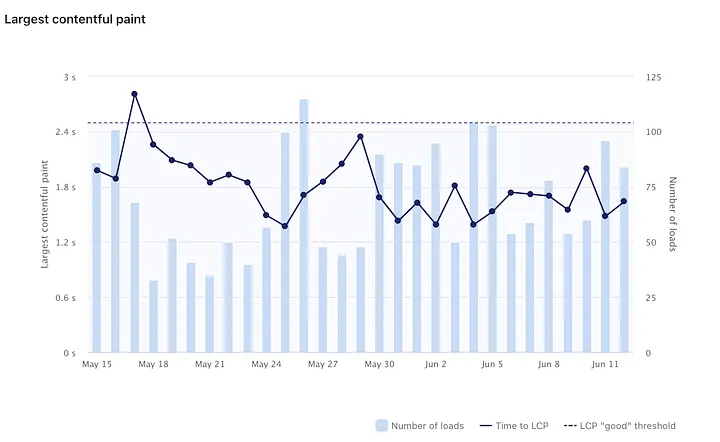
The LCP drops below 2.5s on May 18th, when code splitting was added. It works!
Optimizing the LCP value, as showcased in the case of RealtimeStack, is important for Shopify apps to provide a positive and productive user experience and qualify for the “Built for Shopify” badge. If your LCP value is too high, consider improving it. It will benefit your users and — at least for me — it was a fun, technical challenge.
This article was written by the author of RealtimeStack.